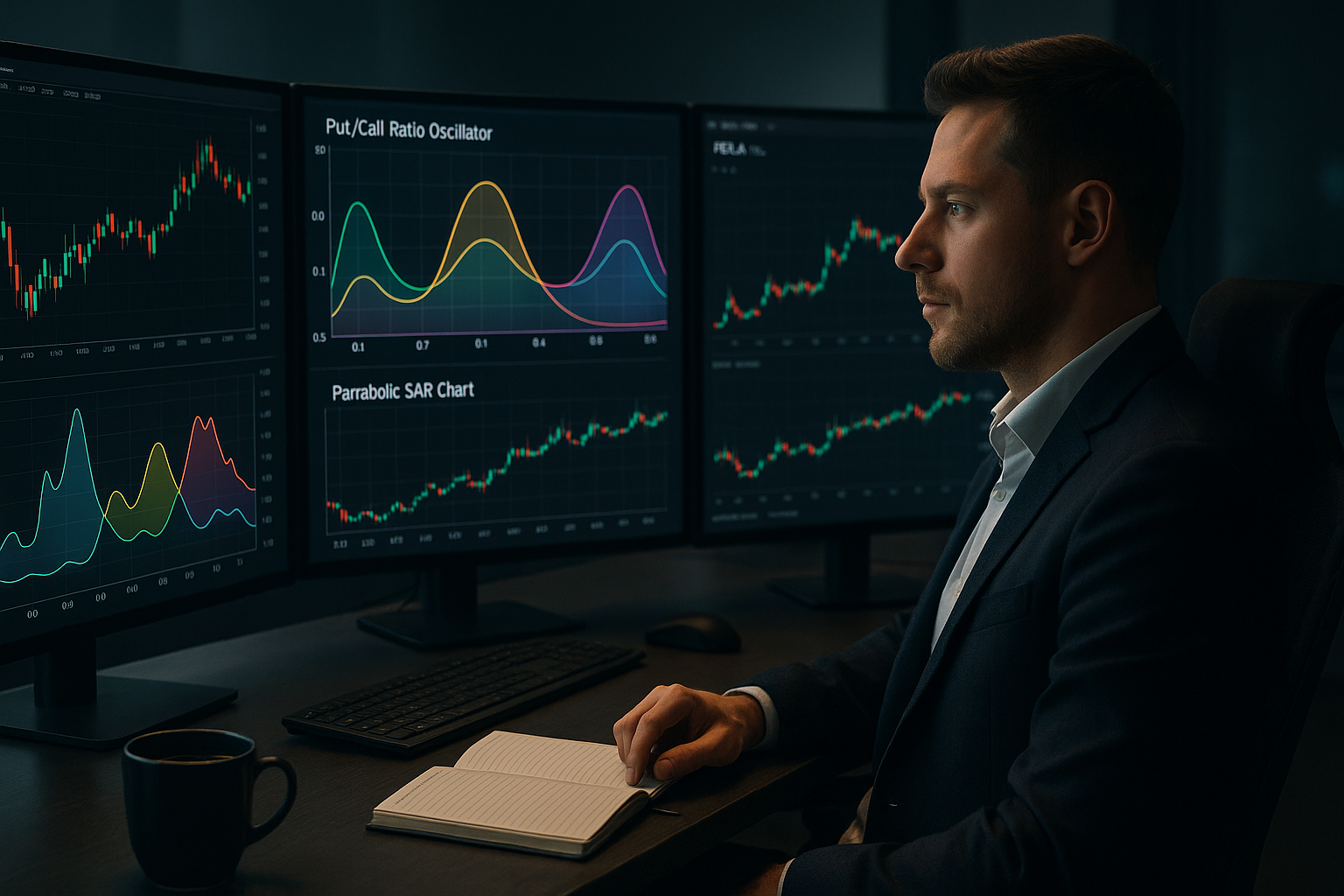
Traders seeking to fine-tune their strategies can gain an edge by tapping into market sentiment. One practical way to do this is by using the put/call ratio, a well-known indicator that reveals the tug-of-war between bearish and bullish forces in the options market. In this article, I’ll walk you through a clever technique that transforms the put/call ratio into an oscillator to complement your existing trading approach.
What Exactly Is the Put/Call Ratio?
The put/call ratio is a simple measure that pits the trading volume of put options—contracts betting on a price drop—against call options, which wager on a price rise. The formula is easy:
- Put/Call Ratio = Put Volume ÷ Call Volume
When the ratio climbs above 1, it means more puts are being traded, hinting at a bearish vibe. A ratio below 1 shows call volume taking the lead, suggesting bullish sentiment. The real value lies in its ability to flag potential turning points: an extremely low ratio might signal overblown optimism, nudging a savvy trader to brace for a market dip.
Creating a Smoother Oscillator
On its own, the put/call ratio can be a wild ride, bouncing around daily and making it tough to rely on. To tame this volatility, we can turn it into an oscillator. Here’s the step-by-step:
- Compute the Average: Find the average put/call ratio over a chosen period, like 30 trading days.
- Set the Boundaries: Look back over a longer window—say, 60 days—to pinpoint the highest and lowest averages.
- Normalize the Data: Scale the current average between these extremes to get a value from 0 to 1 (or 0% to 100%).
Let’s call this the Volume Ratio Average Oscillator (VRAO). It gives a steadier view of sentiment: a value near 1 reflects heavy put trading, while a value near 0 highlights call strength. The magic happens when it shifts away from these extremes, often hinting at a change in market direction.
Using It as a Filter: Supercharging Your Trades
The VRAO isn’t here to call the shots on its own—it’s a sidekick to your trend-following strategy. It helps you ramp up your position when sentiment backs your play. Here’s how it works:
- Going Long: If you’re already in a bullish trade (guided by your main system), the VRAO green-lights adding shares when it dips below a high mark, like 0.9. This drop signals growing call activity, aligning with your upward trend.
- Going Short: If you’re shorting, the VRAO suggests piling on when it rises above a low mark, like 0.1, as put volume picks up, reinforcing the bearish move.
Picture it as a turbo boost: it won’t start your trade, but it helps you lean in when the winds are favorable.
A Tesla Test Run
Let’s see this in action with Tesla stock, paired with the Parabolic SAR, a trend-following tool that plots dots above or below the price—below for bullish trends, above for bearish. Imagine you’re trading Tesla daily:
- Entry Point: The SAR flips from bearish (dots above) to bullish (dots below), so you buy 100 shares.
- VRAO Boost: You’ve set the VRAO with a 30-day average, a 60-day range, and a bullish threshold of 0.9. When it falls below 0.9—showing call volume spiking—you grab another 100 shares. You might repeat this up to four times if the trend holds.
For a short trade:
- Short Entry: The SAR turns bearish, and you short 100 shares. If the VRAO climbs above 0.1, with puts gaining traction, you short another 100.
In a 10-year backtest, the Parabolic SAR alone might net $42,000 over 206 trades. Adding the VRAO could lift that to $78,000 across 270 trades, boosting the risk-reward payoff. But don’t get too excited—historical wins don’t lock in future success.
Why It’s Promising (and Where It Falls Short)
This method thrives by syncing your moves with sentiment swings, potentially juicing profits in clear trends. The oscillator cuts through the noise for a cleaner signal. Still, it’s not perfect:
- Sentiment’s Not the Whole Story: The put/call ratio tracks options trades, not the full market picture.
- Tweak the Dials: The settings (30 days, 0.9, 0.1) might need adjusting for different stocks or conditions.
- Backtests Aren’t Foolproof: What worked yesterday might flop tomorrow.
Ready to Try It?
If you’re curious, here’s how to dive in:
- Choose a trend-following method (like Parabolic SAR or moving averages).
- Build the VRAO with daily put/call data—check your trading platform or options exchanges.
- Pick your settings (e.g., 30-day average, 60-day range, thresholds at 0.9 and 0.1).
- Test it on a stock like Tesla, practice in a simulator, and tweak before trading live.
Pair this oscillator with a solid strategy, and you’ve got a shot at using sentiment to sharpen your trades. Just keep testing and watch your risks!
Want to Automate This for Options?
If you’re interested in automating options trading, check out PickMyTrade.io we support TradeStation and IBKR options trading with full alert-to-execution automation.